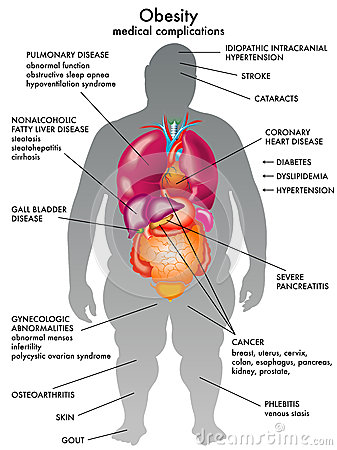
Health Risks Linked to Obesity
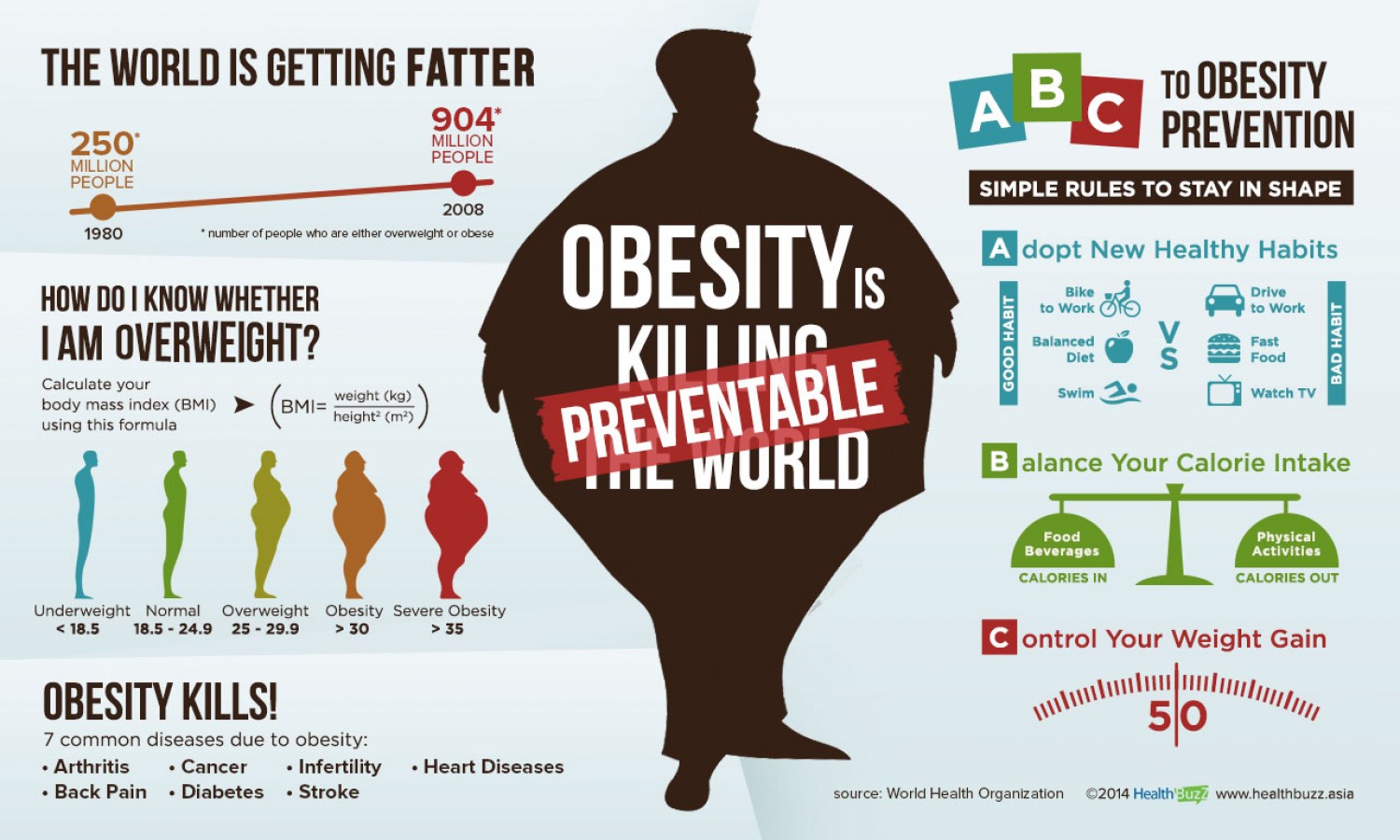
Being obese means that you weigh 20% more than what is considered a normal weight for your height. At your doctor’s office, we calculate something called your BMI (body mass index) to determine if you are underweight (BMI <18.5), normal weight (BMI 18.5–24.9), overweight (BMI 25-29.9), or if you’ve ventured into obesity (BMI greater than or =30).
Obesity has been linked to a multitude of health problems, including but not limited to:
-
Heart disease and stroke
-
High blood pressure
-
High cholesterol
-
Diabetes
-
Gallbladder disease and gallstones
-
Osteoarthritis
-
Gout
-
Sleep Apnea
-
Asthma
-
Some cancers
The upside is that losing a small amount of weight (about 5-10%) can reduce your chances of developing the above. The first step is setting realistic weight loss goals.
Remember:
-
It is recommended by the National Institute of Health (NIH) to try and lose 5 to 10 percent of your current weight over 6 months. This will lower your risk for coronary heart disease (CHD) and other conditions.
-
The best way to lose weight is slowly. A weight loss of 1 to 2 pounds a week is do-able, safe, and will help you keep off the weight. It also will give you the time to make new, healthy lifestyle changes.
-
This is a lifestyle change! You will be working with a combination of diet, exercise, and behavioral modification.
-
If you've lost 10 percent of your body weight, have kept it off for 6 months, and are still overweight or obese, you may want to consider further weight loss.
-
If your BMI is greater than 30, it is worthwhile to be seen by a physician to check if your weight gain is secondary to an underlying medical problem. At the least, your physician can counsel you on great ways to start toward your goal of weight loss and a healthier, better you!
Dr Le's Primary Care Topics